Frequently Asked Questions of MIO Coating and Paints
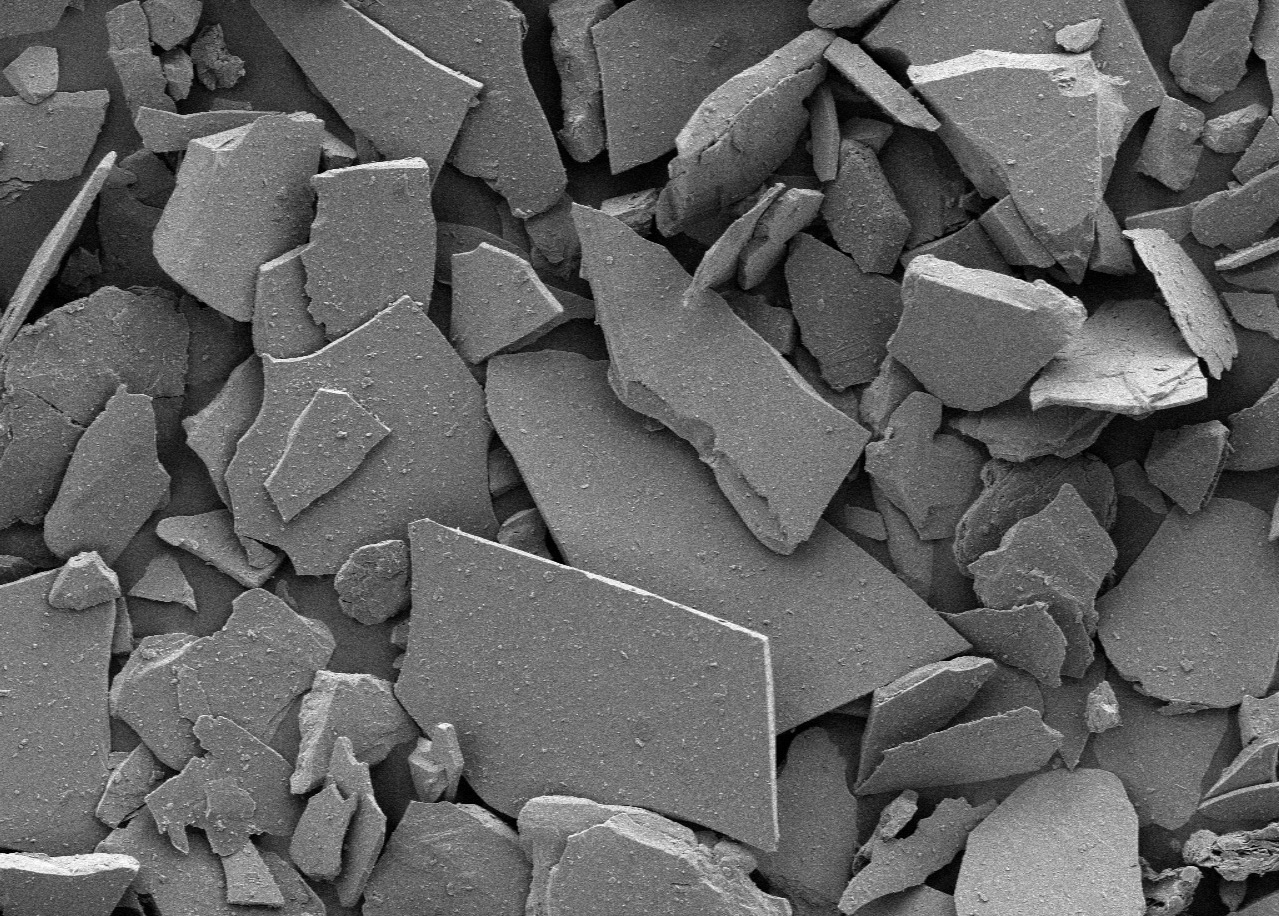
Micaceous Iron Oxide (MIO) is iron oxide in a shape that resembles mica, a mineral with a strong structure and a base. MIO pigments are ground into smaller, finer particles; they appear to cleave up along their layers, exposing smooth, shiny faces that serve as tiny mirrors. Such tiny mirrors capture UV light, protect the resin from oxidation and give an attractive glow to the coating.
MIO is a high-built, two-component epoxy coating that is best suited for exterior applications. It is very tough and resistant to abrasion, and has increased resistance to weather. As the coating dries, the very thin platelet shaped pigment particles orient themselves parallel to the substrate to give an armored effect to the film and also act as an impediment to the diffusion of oxygen and moisture through the film.
Epoxy coating uses a chemical mix of two liquid components, epoxy resin and hardener, to create a tough, solvent-resistant finish that can be applied to floors, countertops and decks. Many types of epoxy are noted for their durability and can be used to seal concrete floors, steel and other industrial materials.
Micaceous iron oxide (MIO) is a naturally occurring mineral material and is used as the primary ingredient in certain protective coatings and primers because of its anti-corrosive properties. When it is added to a coating and applied to the substrate the flakes align parallel to the surface creating an impermeable barrier to water, oxygen and chemicals. The flakes are strong UV absorbers and extremely weather resistant.































































































.png)




